
- Current
- Browse
- Collections
-
For contributors
- For Authors
- Instructions to authors
- Article processing charge
- e-submission
- For Reviewers
- Instructions for reviewers
- How to become a reviewer
- Best reviewers
- For Readers
- Readership
- Subscription
- Permission guidelines
- About
- Editorial policy
Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- Metabolic Risk/Epidemiology
- Insulin Resistance Increases Serum Immunoglobulin E Sensitization in Premenopausal Women
- Seung Eun Lee, Ji Yeon Baek, Kyungdo Han, Eun Hee Koh
- Diabetes Metab J. 2021;45(2):175-182. Published online April 14, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2019.0150
- 6,208 View
- 123 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 1 Crossref
-
 Graphical Abstract
Graphical Abstract
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub 
Background Although studies have shown that obesity is associated with aeroallergen sensitization (atopy), controversy still exists. We aimed to investigate the association between metabolic status, obesity, and atopy stratified by sex and menopausal status.
Methods A total of 1,700 adults from the 2010 Korean National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey were classified into metabolically healthy nonobese (MHNO), metabolically unhealthy nonobese (MUNO), metabolically healthy obese (MHO), and metabolically unhealthy obese (MUO) by body mass index and insulin resistance. Atopy was defined as a positive response to at least one aeroallergen. Multiple regression analysis was used to evaluate the risk of immunoglobulin E (IgE) elevation or atopy in relation to the degree of metabolic abnormality and obesity.
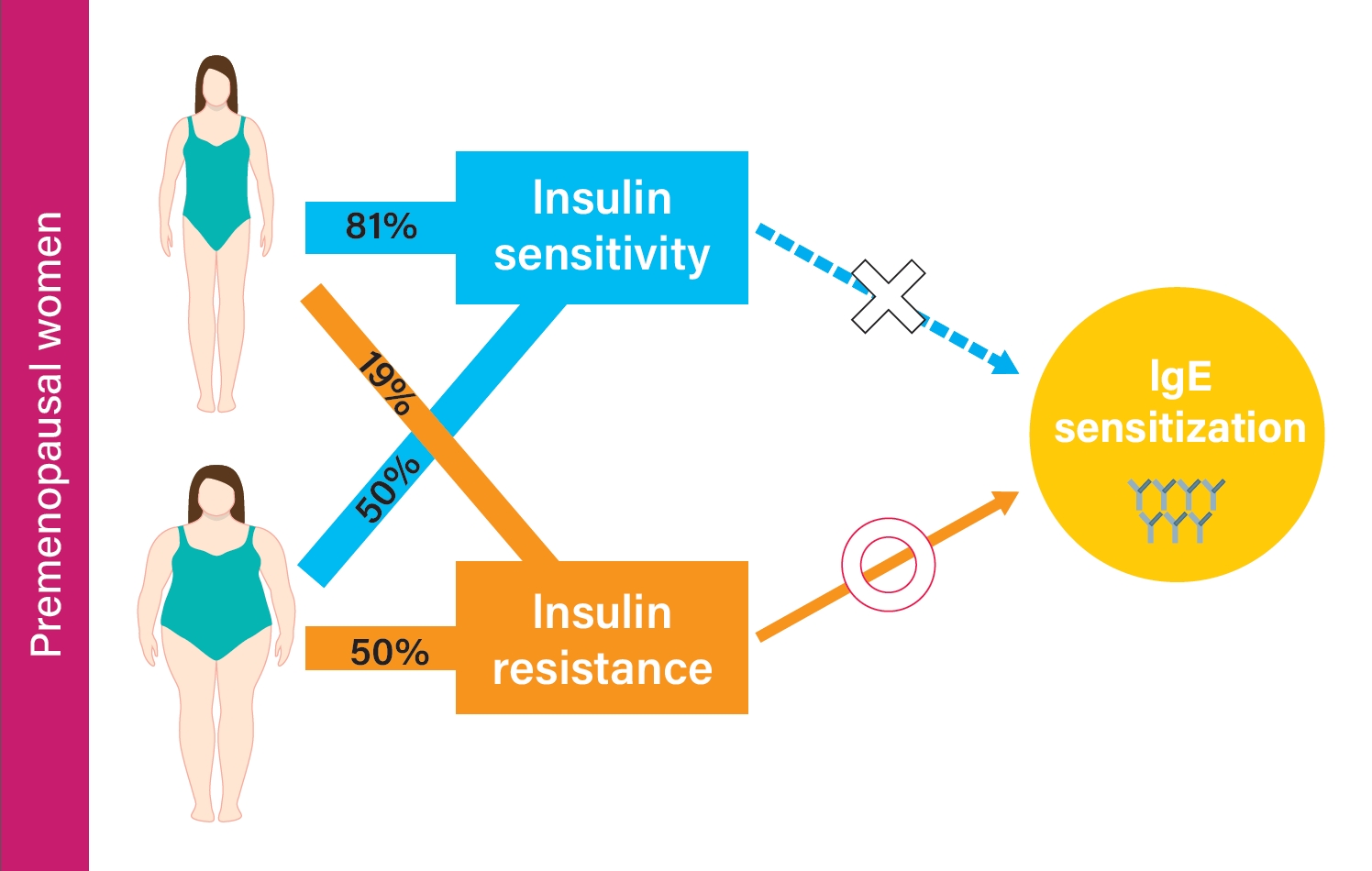
Results In premenopausal women, total IgE was positively correlated with obesity and insulin resistance. MUNO participants had a higher risk of having elevated total IgE compared to MHNO participants (odds ratio [OR], 2.271; 95% confidence interval [CI], 1.201 to 4.294), while MHO participants did not show a significant difference (OR, 1.435; 95% CI, 0.656 to 3.137) in premenopausal women. MUNO, but not MHO was also associated with atopy (OR, 2.157; 95% CI, 1.284 to 3.625). In men and postmenopausal women, there was no significant difference between metabolic status, obesity, and atopy among groups.
Conclusion Increased insulin resistance is associated with total IgE and atopy in premenopausal women but not in postmenopausal women or men.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Is There a Relationship between Insulin Resistance and Eosinophil, Inflammatory Parameters Neutrophil to lymphocyte ratio, C-Reactive Protein Values?
Meltem YİĞİT, Özgür OLUKMAN
Medical Records.2024; 6(1): 32. CrossRef
- Is There a Relationship between Insulin Resistance and Eosinophil, Inflammatory Parameters Neutrophil to lymphocyte ratio, C-Reactive Protein Values?
- Basic Research
-
- Inhibition of Ceramide Accumulation in Podocytes by Myriocin Prevents Diabetic Nephropathy
- Chang-Yun Woo, Ji Yeon Baek, Ah-Ram Kim, Chung Hwan Hong, Ji Eun Yoon, Hyoun Sik Kim, Hyun Ju Yoo, Tae-Sik Park, Ranjan Kc, Ki-Up Lee, Eun Hee Koh
- Diabetes Metab J. 2020;44(4):581-591. Published online November 4, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2019.0063
- 6,178 View
- 165 Download
- 26 Web of Science
- 29 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub Background Ceramides are associated with metabolic complications including diabetic nephropathy in patients with diabetes. Recent studies have reported that podocytes play a pivotal role in the progression of diabetic nephropathy. Also, mitochondrial dysfunction is known to be an early event in podocyte injury. Thus, we tested the hypothesis that ceramide accumulation in podocytes induces mitochondrial damage through reactive oxygen species (ROS) production in patients with diabetic nephropathy.
Methods We used Otsuka Long Evans Tokushima Fatty (OLETF) rats and high-fat diet (HFD)-fed mice. We fed the animals either a control- or a myriocin-containing diet to evaluate the effects of the ceramide. Also, we assessed the effects of ceramide on intracellular ROS generation and on podocyte autophagy in cultured podocytes.
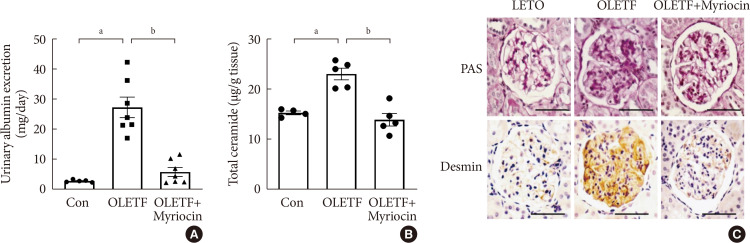
Results OLETF rats and HFD-fed mice showed albuminuria, histologic features of diabetic nephropathy, and podocyte injury, whereas myriocin treatment effectively treated these abnormalities. Cultured podocytes exposed to agents predicted to be risk factors (high glucose, high free fatty acid, and angiotensin II in combination [GFA]) showed an increase in ceramide accumulation and ROS generation in podocyte mitochondria. Pretreatment with myriocin reversed GFA-induced mitochondrial ROS generation and prevented cell death. Myriocin-pretreated cells were protected from GFA-induced disruption of mitochondrial integrity.
Conclusion We showed that mitochondrial ceramide accumulation may result in podocyte damage through ROS production. Therefore, this signaling pathway could become a pharmacological target to abate the development of diabetic kidney disease.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Interplay of lipid metabolism and inflammation in podocyte injury
Zilv Luo, Zhaowei Chen, Jijia Hu, Guohua Ding
Metabolism.2024; 150: 155718. CrossRef - Associations of plasma sphingolipids with measures of insulin sensitivity, β-cell function, and incident diabetes in Japanese Americans
Ji Cheol Bae, Pandora L. Wander, Rozenn N. Lemaitre, Amanda M. Fretts, Colleen M. Sitlani, Hai H. Bui, Melissa K. Thomas, Donna Leonetti, Wilfred Y. Fujimoto, Edward J. Boyko, Kristina M. Utzschneider
Nutrition, Metabolism and Cardiovascular Diseases.2024; 34(3): 633. CrossRef - A review of the mechanisms of abnormal ceramide metabolism in type 2 diabetes mellitus, Alzheimer’s disease, and their co-morbidities
Yun Pan, Jieying Li, Panjie Lin, Lihua Wan, Yiqian Qu, Lingyong Cao, Lei Wang
Frontiers in Pharmacology.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Ceramides and mitochondrial homeostasis
Song Ding, Guorui Li, Tinglv Fu, Tianyu Zhang, Xiao Lu, Ning Li, Qing Geng
Cellular Signalling.2024; 117: 111099. CrossRef - Reduced sphingolipid biosynthesis modulates proteostasis networks to enhance longevity
Nathaniel L. Hepowit, Eric Blalock, Sangderk Lee, Kimberly M. Bretland, Jason A. MacGurn, Robert C. Dickson
Aging.2023; 15(2): 472. CrossRef - Protective effect of natural products in the metabolic-associated kidney diseases via regulating mitochondrial dysfunction
Peng Liu, Yao Chen, Jing Xiao, Wenhui Zhu, Xiaoming Yan, Ming Chen
Frontiers in Pharmacology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - BCAA insufficiency leads to premature ovarian insufficiency via ceramide‐induced elevation of ROS
Xiao Guo, Yuemeng Zhu, Lu Guo, Yiwen Qi, Xiaocheng Liu, Jinhui Wang, Jiangtao Zhang, Linlin Cui, Yueyang Shi, Qichu Wang, Cenxi Liu, Guangxing Lu, Yilian Liu, Tao Li, Shangyu Hong, Yingying Qin, Xuelian Xiong, Hao Wu, Lin Huang, He Huang, Chao Gu, Bin Li,
EMBO Molecular Medicine.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Chinese herbal medicine and its active compounds in attenuating renal injury via regulating autophagy in diabetic kidney disease
Peng Liu, Wenhui Zhu, Yang Wang, Guijie Ma, Hailing Zhao, Ping Li
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Integrated gas chromatography‐mass spectrometry and ultra‐high‐performance liquid chromatography‐mass spectrometry renal metabolomics and lipidomics deciphered the metabolic regulation mechanism of Gushudan on kidney‐yang‐deficiency‐syndrome rats
Qing Lu, Jing Zhang, Ling Xin, Yanwei Lou, Feng Qin, Longshan Zhao, Zhili Xiong
Journal of Separation Science.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Advances in the pharmacological study of Chinese herbal medicine to alleviate diabetic nephropathy by improving mitochondrial oxidative stress
Ming Chen, Yao Chen, Wenhui Zhu, Xiaoming Yan, Jing Xiao, Peiqing Zhang, Peng Liu, Ping Li
Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy.2023; 165: 115088. CrossRef - Rodent models to study type 1 and type 2 diabetes induced human diabetic nephropathy
Amit Talukdar, Mandira Basumatary
Molecular Biology Reports.2023; 50(9): 7759. CrossRef - Art2 mediates selective endocytosis of methionine transporters during adaptation to sphingolipid depletion
Nathaniel L. Hepowit, Bradley Moon, Adam C. Ebert, Robert C. Dickson, Jason A. MacGurn
Journal of Cell Science.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Kidney lipid dysmetabolism and lipid droplet accumulation in chronic kidney disease
Alla Mitrofanova, Sandra Merscher, Alessia Fornoni
Nature Reviews Nephrology.2023; 19(10): 629. CrossRef - Research progress of autophagy in pathogenesis of diabetes nephropathy
Shengnan Zeng, Ying Li
Diabetic Nephropathy.2023; 3(3): 51. CrossRef - Lipidomic approaches to dissect dysregulated lipid metabolism in kidney disease
Judy Baek, Chenchen He, Farsad Afshinnia, George Michailidis, Subramaniam Pennathur
Nature Reviews Nephrology.2022; 18(1): 38. CrossRef - Podocyte Bioenergetics in the Development of Diabetic Nephropathy: The Role of Mitochondria
Irena Audzeyenka, Agnieszka Bierżyńska, Abigail C Lay
Endocrinology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Acylcarnitines: Can They Be Biomarkers of Diabetic Nephropathy?
Xiaodie Mu, Min Yang, Peiyao Ling, Aihua Wu, Hua Zhou, Jingting Jiang
Diabetes, Metabolic Syndrome and Obesity: Targets and Therapy.2022; Volume 15: 247. CrossRef - Research Progress on Natural Products’ Therapeutic Effects on Atrial Fibrillation by Regulating Ion Channels
Jinshan He, Sicong Li, Yumeng Ding, Yujia Tong, Xuebin Li, Simona Saponara
Cardiovascular Therapeutics.2022; 2022: 1. CrossRef - Mechanisms of podocyte injury and implications for diabetic nephropathy
Federica Barutta, Stefania Bellini, Gabriella Gruden
Clinical Science.2022; 136(7): 493. CrossRef - A Rheostat of Ceramide and Sphingosine-1-Phosphate as a Determinant of Oxidative Stress-Mediated Kidney Injury
Norishi Ueda
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2022; 23(7): 4010. CrossRef - Implications of Sphingolipid Metabolites in Kidney Diseases
Shamroop kumar Mallela, Sandra Merscher, Alessia Fornoni
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2022; 23(8): 4244. CrossRef - Role of ceramides in the pathogenesis of diabetes mellitus and its complications
Nawajes Mandal, Richard Grambergs, Koushik Mondal, Sandip K. Basu, Faiza Tahia, Sam Dagogo-Jack
Journal of Diabetes and its Complications.2021; 35(2): 107734. CrossRef - Rotten to the Cortex: Ceramide-Mediated Lipotoxicity in Diabetic Kidney Disease
Rebekah J. Nicholson, Marcus G. Pezzolesi, Scott A. Summers
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Enhancing lifespan of budding yeast by pharmacological lowering of amino acid pools
Nathaniel L. Hepowit, Jessica K. A. Macedo, Lyndsay E. A. Young, Ke Liu, Ramon C. Sun, Jason A. MacGurn, Robert C. Dickson
Aging.2021; 13(6): 7846. CrossRef - New insights into renal lipid dysmetabolism in diabetic kidney disease
Alla Mitrofanova, George Burke, Sandra Merscher, Alessia Fornoni
World Journal of Diabetes.2021; 12(5): 524. CrossRef - Excessively Enlarged Mitochondria in the Kidneys of Diabetic Nephropathy
Kiyoung Kim, Eun-Young Lee
Antioxidants.2021; 10(5): 741. CrossRef - Mechanistic insights into the role of serum-glucocorticoid kinase 1 in diabetic nephropathy: A systematic review
Saba Noor, Taj Mohammad, Gulam M. Ashraf, Joviana Farhat, Anwar L. Bilgrami, Mathew Suji Eapen, Sukhwinder Singh Sohal, Dharmendra Kumar Yadav, Md Imtaiyaz Hassan
International Journal of Biological Macromolecules.2021; 193: 562. CrossRef - The Updates of Podocyte Lipid Metabolism in Proteinuric Kidney Disease
Yu Sun, Sijia Cui, Yunfeng Hou, Fan Yi
Kidney Diseases.2021; 7(6): 438. CrossRef - Saturated fatty acids induce insulin resistance in podocytes through inhibition of IRS1 via activation of both IKKβ and mTORC1
Benoit Denhez, Marina Rousseau, Crysta Spino, David-Alexandre Dancosst, Marie-Ève Dumas, Andréanne Guay, Farah Lizotte, Pedro Geraldes
Scientific Reports.2020;[Epub] CrossRef
- Interplay of lipid metabolism and inflammation in podocyte injury

 KDA
KDA
 First
First Prev
Prev





